When designing a bathroom to be compliant with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), it’s essential to pay close attention to the dimensions and placement of the bathroom sink. The ADA provides guidelines to ensure that facilities are accessible to individuals with disabilities, ensuring they can use the space comfortably and safely. Understanding these guidelines is crucial for architects, designers, and homeowners who want to create inclusive and accessible spaces.
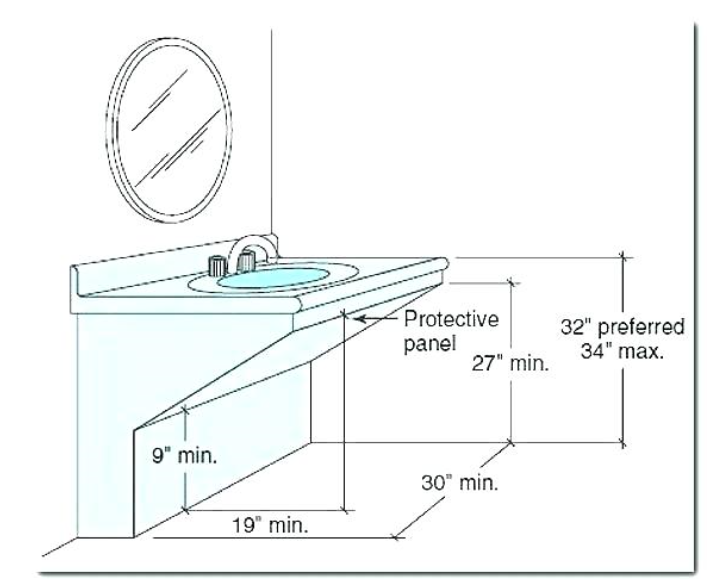
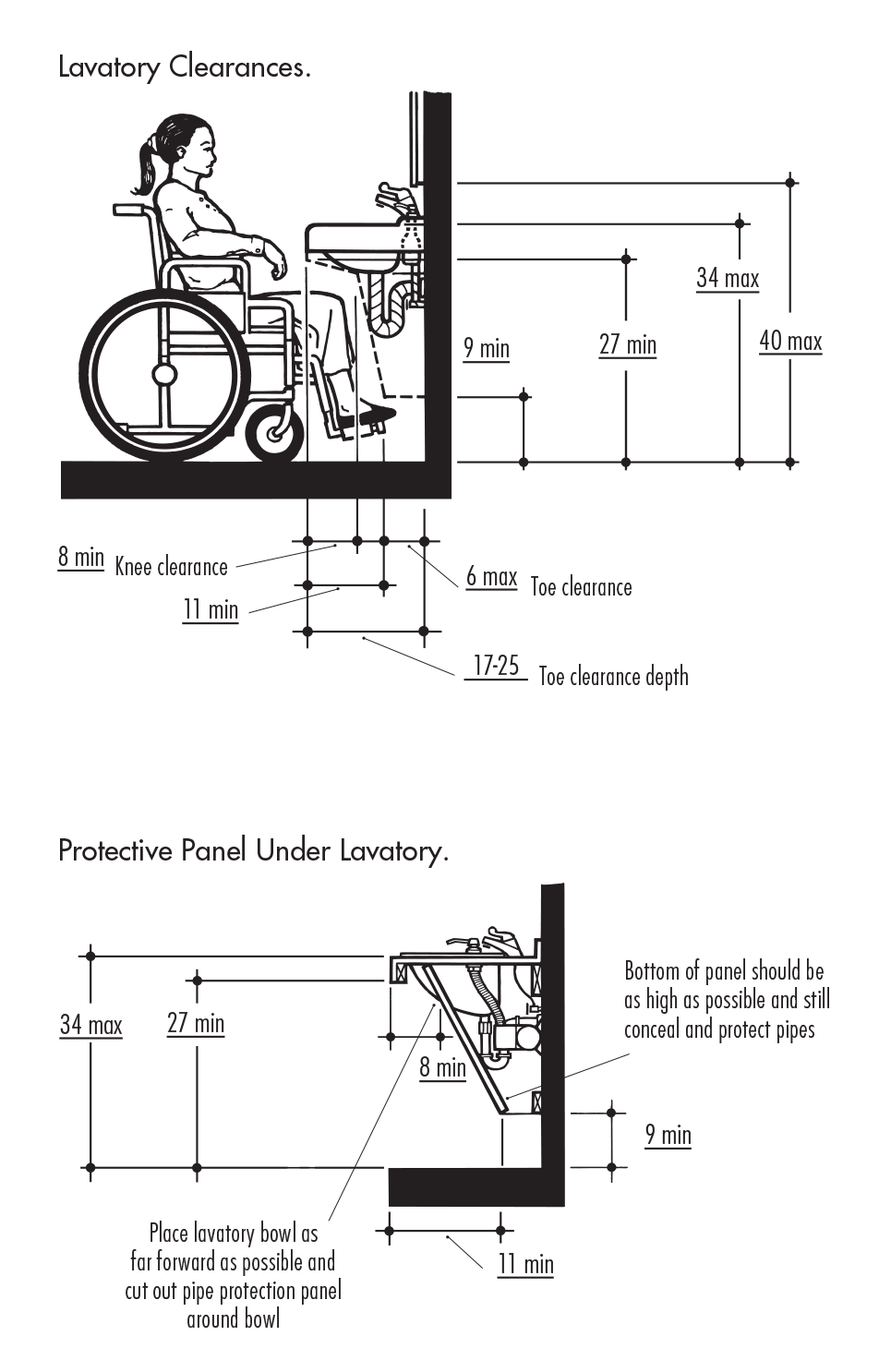
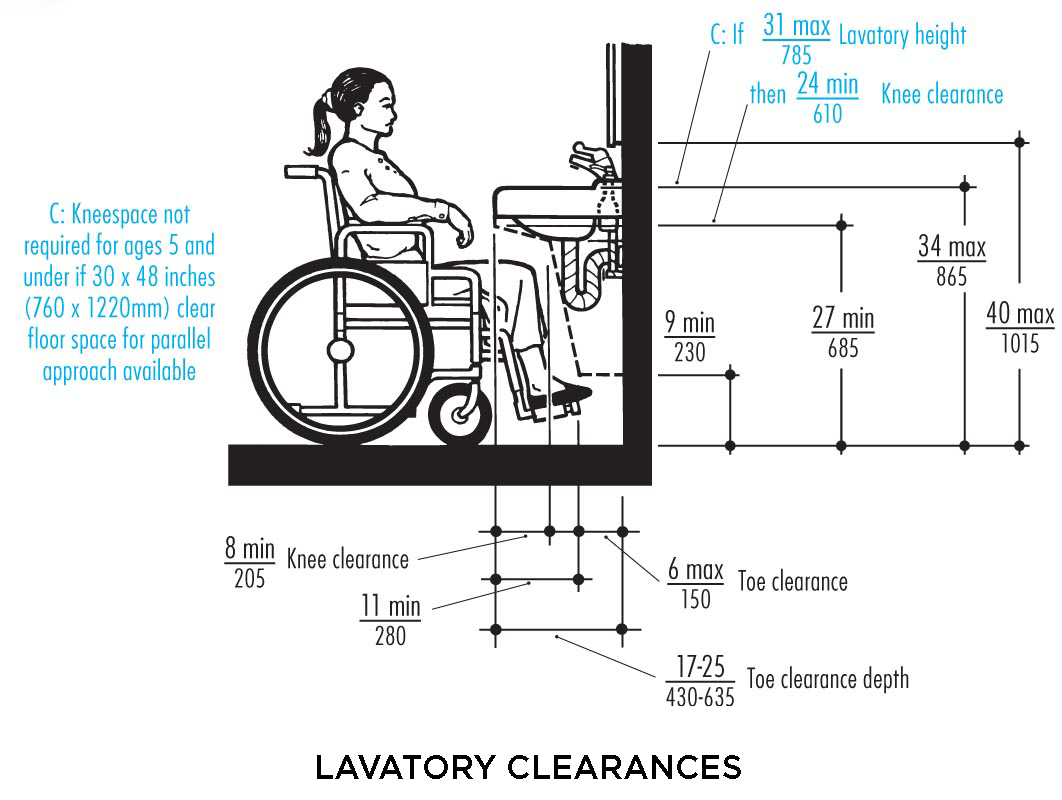
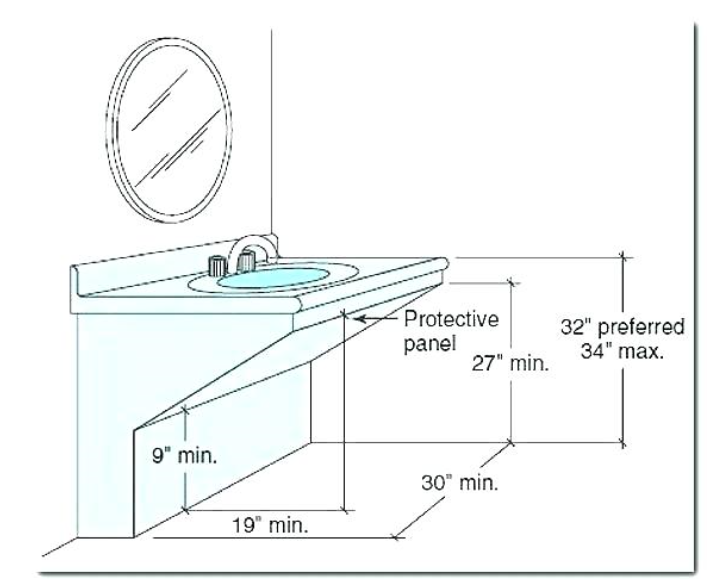
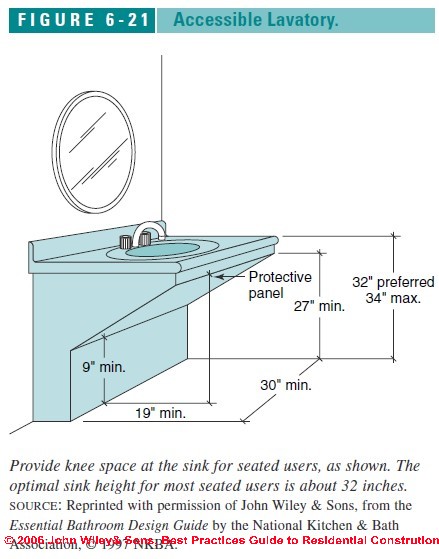
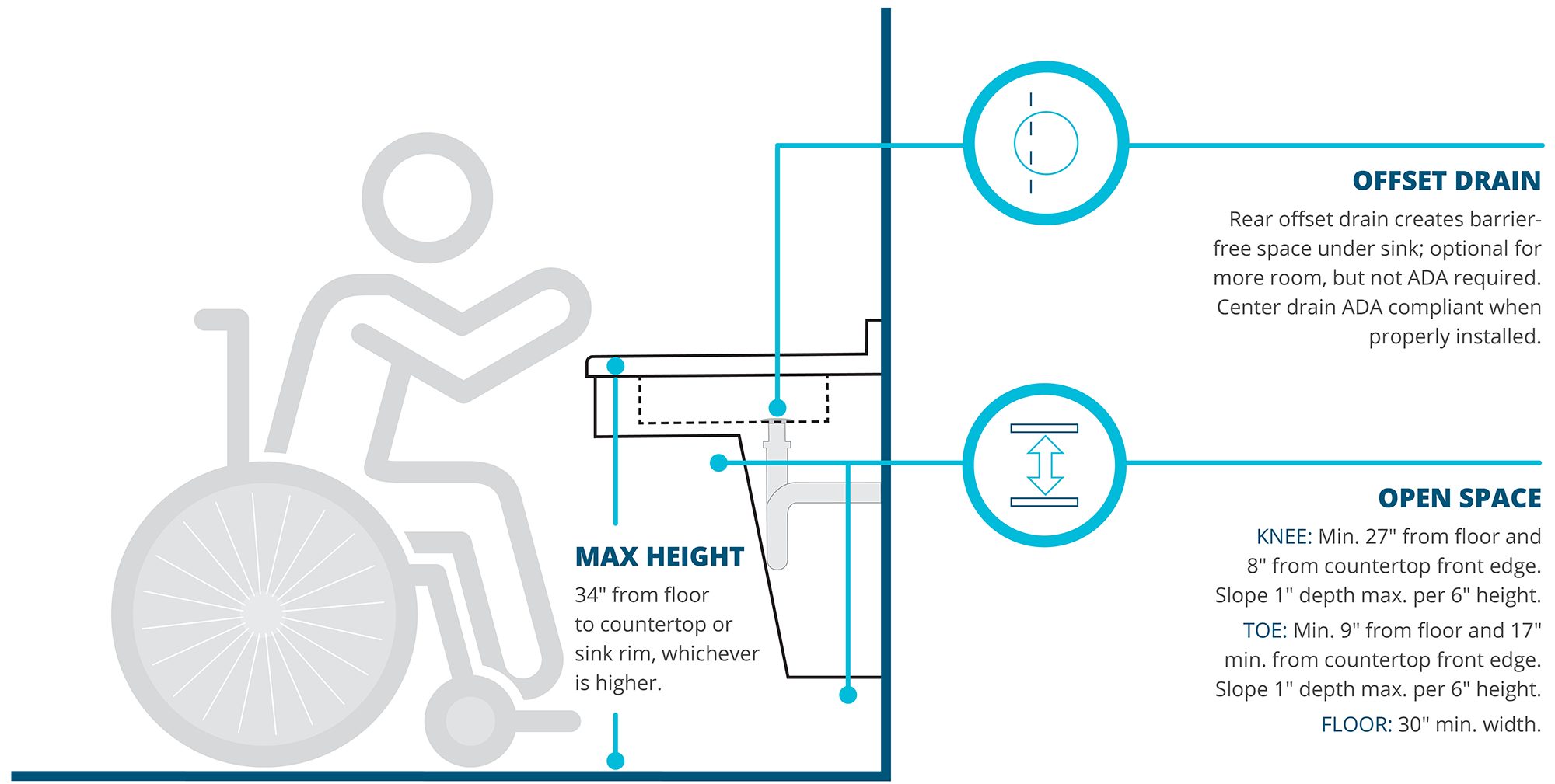
The ADA specifies that the sink height should be no more than 34 inches from the floor to the top of the sink. This height allows individuals who use wheelchairs to comfortably reach the sink and use it without strain. The clearance underneath the sink is equally important; it should be at least 27 inches high, 30 inches wide, and 19 inches deep to accommodate a wheelchair. This provides enough space for the user’s legs and allows them to roll up to the sink.
In addition to the height and clearance requirements, the ADA also specifies the depth of the sink. The depth should not exceed 6.5 inches to allow for easy access to the faucet and sink basin. This shallow depth helps prevent individuals from having to reach too far, which can be difficult for those with limited mobility. The sink should also have a clear space of at least 30 by 48 inches in front of it to allow for easy approach and maneuverability.
Faucet controls are another important consideration. ADA-compliant faucets should be operable with one hand and not require tight grasping, pinching, or twisting of the wrist. Lever-operated, push-type, or electronically controlled mechanisms are ideal. These types of faucets make it easier for individuals with limited hand dexterity to use the sink. Additionally, the faucet should be positioned so that it is within easy reach from a seated position.
The placement of the sink and surrounding fixtures is also crucial. The ADA requires that there be a clear floor space around the sink, allowing for forward or side approach. This ensures that individuals using wheelchairs have enough room to navigate and use the sink comfortably. This space should be free of obstructions, such as cabinets or other fixtures, to allow for easy access.
Mirrors and dispensers near the sink must also be installed at an accessible height. The bottom edge of the mirror should be no more than 40 inches above the floor to allow individuals in wheelchairs to use it. Similarly, soap dispensers, hand dryers, and other accessories should be within easy reach, typically mounted no higher than 48 inches from the floor. These considerations help create a fully accessible environment.
The materials and finishes used in an ADA-compliant bathroom sink area are also important. Non-slip surfaces on the floor can help prevent accidents, while smooth, rounded edges on the sink and countertops reduce the risk of injury. The sink itself should be sturdy and well-secured to handle the weight and pressure of users leaning on it for support.
In addition to these physical dimensions, it’s also important to consider the overall design and layout of the bathroom. The sink should be positioned in a location that is easy to access from the entrance of the bathroom, without requiring sharp turns or difficult maneuvers. Good lighting around the sink area is also essential, as it helps individuals with visual impairments use the sink more effectively.
When selecting a sink, there are many ADA-compliant options available, including wall-mounted sinks, which are often the most accessible choice as they provide clear space underneath for wheelchair users. Pedestal sinks, while aesthetically pleasing, often do not meet ADA requirements due to the lack of knee and toe clearance. Integrated countertops with built-in sinks can also be a good choice, provided they meet the required dimensions.
Retrofitting an existing bathroom to make it ADA-compliant can be challenging, but it is often necessary to ensure accessibility. This process might involve adjusting the height of the sink, installing a new faucet, or reconfiguring the space to provide adequate clearance. While these modifications can be costly, they are essential for creating a space that is usable by everyone, regardless of their physical abilities.
Public restrooms must adhere to ADA guidelines, but private homes can also benefit from following these standards. An accessible bathroom in a home not only accommodates residents with disabilities but also ensures that guests can use the facilities comfortably. This consideration is particularly important in multigenerational households or homes where elderly family members live.
Creating an ADA-compliant bathroom sink area also involves considering the needs of individuals with different types of disabilities. For example, individuals with limited strength may need additional supports, such as grab bars, to help them use the sink safely. Similarly, those with visual impairments might benefit from contrasting colors and tactile indicators to help them locate and use the sink.
Another key aspect of ADA compliance is regular maintenance. Ensuring that the sink, faucets, and surrounding areas are kept in good condition is essential for maintaining accessibility. This includes promptly repairing any damage, ensuring that fixtures are securely attached, and keeping the area clean and free of obstructions.
Ultimately, designing a bathroom with an ADA-compliant sink involves careful planning and attention to detail. By following the guidelines and considering the specific needs of users, it’s possible to create a space that is not only functional but also welcoming and inclusive. Whether in a public building or a private home, an ADA-compliant bathroom sink enhances accessibility and ensures that everyone can use the facilities with ease and dignity.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
When creating an ADA-compliant bathroom sink area, there are several common mistakes that can compromise accessibility. One major mistake is not providing enough knee clearance under the sink. ADA guidelines require at least 27 inches of vertical clearance, but failing to meet this requirement can make the sink unusable for wheelchair users. Ensuring sufficient space is crucial for comfort and accessibility.
Another frequent error is installing the sink too high or too low. The sink height should be no more than 34 inches from the floor. Sinks installed outside this range can be difficult or impossible for some users to reach. It’s important to measure accurately and adhere to the specified dimensions.
Using faucets that are difficult to operate is another common mistake. ADA-compliant faucets should be easy to use without tight grasping, pinching, or twisting of the wrist. Lever handles, touchless sensors, or push-button controls are ideal. Installing traditional round knobs can make the sink inaccessible for individuals with limited hand mobility.
Neglecting to provide clear floor space around the sink can also hinder accessibility. ADA guidelines require a clear space of at least 30 by 48 inches to allow for forward or side approach. Placing cabinets, bins, or other obstructions in this area can prevent wheelchair users from reaching the sink comfortably.
Finally, overlooking the importance of proper lighting is a mistake. Good lighting is essential for individuals with visual impairments to use the sink effectively. Ensuring that the sink area is well-lit can enhance accessibility and safety.
What are the ADA height requirements for bathroom sinks?
The ADA specifies that bathroom sinks should be installed no higher than 34 inches from the floor to the top of the sink. This height allows individuals who use wheelchairs to comfortably reach and use the sink. Additionally, there must be a clearance of at least 27 inches from the floor to the underside of the sink to accommodate wheelchair users’ knees and legs.
How much clearance is required under an ADA-compliant sink?
ADA guidelines require a clearance of at least 27 inches high, 30 inches wide, and 19 inches deep under the sink. This space provides enough room for wheelchair users to roll up to the sink and use it comfortably. Proper clearance ensures that individuals with disabilities can approach the sink and use it without obstructions.
What types of faucets are ADA-compliant?
ADA-compliant faucets must be operable with one hand and should not require tight grasping, pinching, or twisting of the wrist. Lever-operated faucets, push-type controls, and touchless sensors are ideal choices. These types of faucets are designed to be easy to use for individuals with limited hand dexterity and strength.
Can pedestal sinks be ADA-compliant?
Pedestal sinks typically do not meet ADA requirements because they lack the necessary knee and toe clearance underneath. ADA-compliant sinks should have open space beneath to allow for wheelchair access. Wall-mounted sinks are often a better choice for ADA compliance as they provide the required clearance and are easier to access for wheelchair users.
How can I make my home bathroom sink ADA-compliant?
To make a home bathroom sink ADA-compliant, ensure that the sink height is no more than 34 inches from the floor, and provide at least 27 inches of vertical clearance underneath. Install a faucet that is easy to operate with one hand, such as a lever handle or touchless sensor. Ensure there is a clear floor space of at least 30 by 48 inches in front of the sink. Additionally, mount mirrors and dispensers at accessible heights, typically no higher than 40 inches from the floor for mirrors and 48 inches for dispensers.
Accessible Bath Design: Accessible Bathroom design, layouts
ADA-Compliant Products Elkay
ADA Bathroom Sinks KralSu Sink and Faucet Supplies
Related articles:
- Bathroom Sink Clogged Drano
- Unclogging Bathroom Sink With Vinegar And Baking Soda
- Miranda Lambert Bathroom Sink Meaning
- Bathroom Sink Vanity Corner
- Delta Bathroom Sink Faucet Parts
- Copper Bathroom Sinks
- Small Countertop Bathroom Sinks
- Bathroom Sink One Bowl Two Faucets
- Bathroom Sink Backsplash Height
- Mini Pedestal Bathroom Sinks